
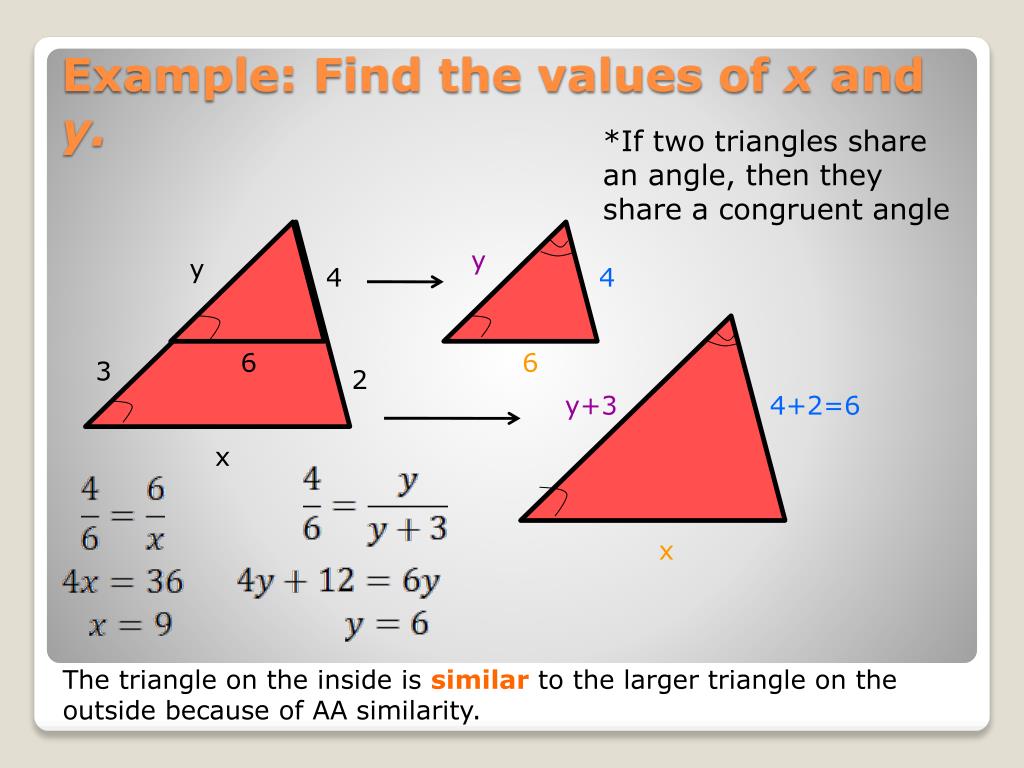
When you've got two triangles and the ratio of two of their sides are the same, plus one of their angles are equal, you can prove that the two triangles are similar.
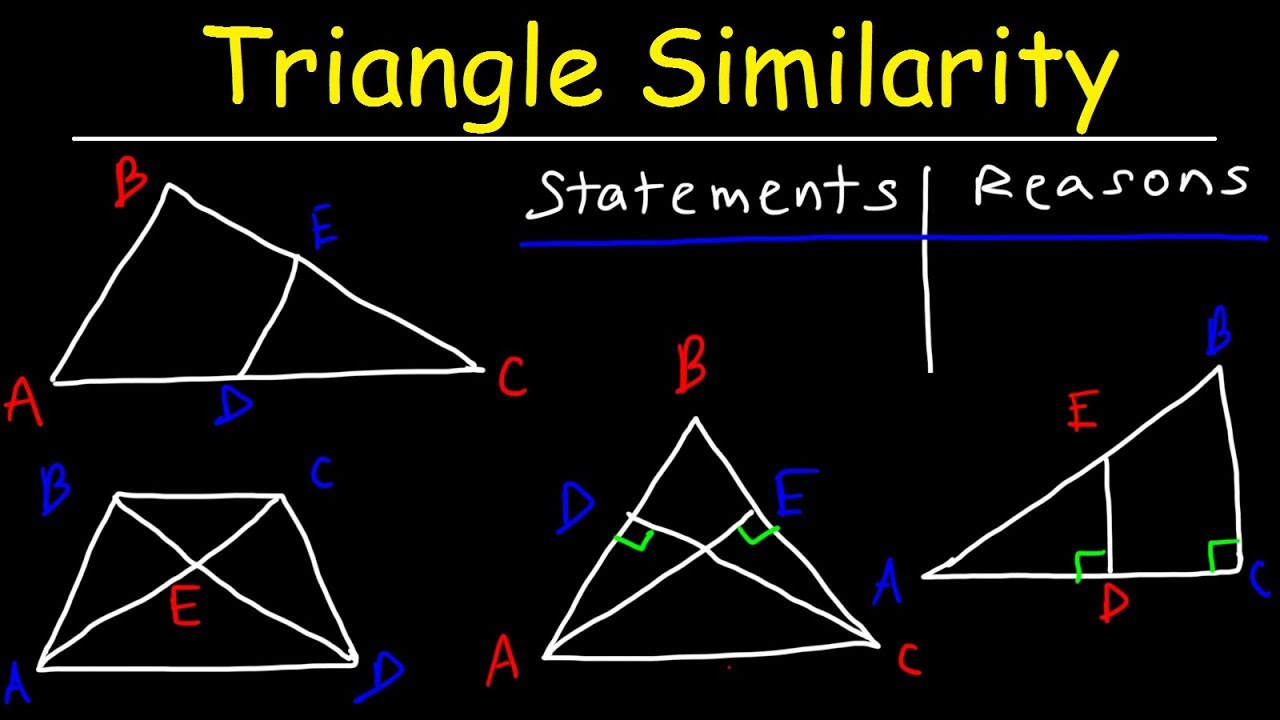
What is the SAS similarity theorem? The SAS similarity theorem stands for side angle side. If two triangles have three pairs of sides in the same ratio, then the triangles are similar. SSS stands for “side, side, side” and means that we have two triangles with all three pairs of corresponding sides in the same ratio. How do you know if SSS triangles are similar? Using this postulate, we no longer have to show that all three corresponding angles of two triangles are equal to prove they are similar. The postulate states that two triangles are similar if they have two corresponding angles that are congruent or equal in measure. … However, the side-side-angle or angle-side -side configurations don't ensure similarity. Is Asa a similarity postulate? For the configurations known as angle-angle-side (AAS), angle-side-angle (ASA) or side-angle-angle (SAA), it doesn't matter how big the sides are the triangles will always be similar. SAA ( angle-side-angle) Two angles and the side between them are congruent. SAS-similarity.Īlso What is ASA similarity? The Angle-Side-Angle Postulate (ASA) states that if two angles and the included side of one triangle are congruent to two angles and the included side of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. if three sides of one triangle are proportional to three corresponding sides of another triangle, then the triangles are similar. if two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the triangles are similar. SAS (side-angle-side) Two sides and the angle between them are congruent.ĪSA (angle-side-angle) Two angles and the side between them are congruent.ĪAS (angle-angle-side) Two angles and a non-included side are congruent.ĪA-similarity. What is ASA similarity theorem? key idea SSS (side-side-side) All three corresponding sides are congruent.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
